To become a wholesaler on Shopify, start by registering your business, securing required licenses, and sourcing your products. Then build your Shopify store, create a wholesale signup page for business customers, set up wholesale pricing, and promote your offerings to attract qualified buyers.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover exactly how to become a wholesaler on Shopify, from choosing the right product niche to scaling your operations efficiently. Whether you’re starting with $5,000 or $50,000, this step-by-step roadmap will help you build a profitable wholesale business in 2026.

Understanding Wholesale Business Basics
Learning how to become a wholesaler has never been more accessible, especially with Shopify’s powerful B2B tools making it easier than ever to enter the wholesale market. Unlike traditional retail that focuses on individual consumers, wholesale businesses operate in the lucrative B2B space, selling products in bulk to retailers, businesses, and commercial establishments.
The wholesale industry continues to grow, with B2B ecommerce expected to reach $25.6 trillion by 2028. This presents a massive opportunity for entrepreneurs looking to build scalable, relationship-driven businesses with predictable revenue streams.
What is a Wholesale Business?
A wholesale business operates on a fundamentally different principle than retail: instead of selling individual products to consumers, wholesalers purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers and resell them in smaller quantities to retailers, businesses, and commercial establishments. This B2B (business-to-business) model makes wholesalers crucial intermediaries in the supply chain.
The core value proposition of wholesaling centers on three key elements:
- Bulk purchasing power that enables negotiated pricing with manufacturers
- Inventory management across multiple product lines and suppliers
- Distribution networks that efficiently move goods from production to retail outlets
Wholesalers profit not from high per-unit margins, but from the volume of transactions. By consolidating purchasing power and providing storage, logistics, and customer service, they create mutual value for manufacturers, retailers, and ultimately consumers.
Transform your B2B store with B2Bridge.
Discover how B2Bridge can transform your wholesale business.
Schedule a demo today to see our payment management tools in action.
Wholesale vs Retail: Key Differences
| Aspect | Wholesale | Retail |
| Target Customers | Businesses, retailers, commercial users | End consumers |
| Order Quantities | Bulk purchases (hundreds/thousands) | Individual units |
| Pricing Structure | Volume-based discounts, net terms | Fixed retail prices |
| Relationship Type | Long-term B2B partnerships | Individual transactions |
| Profit Margins | Lower per unit, higher volume | Higher per unit, lower volume |
Understanding these distinctions is essential before launching your wholesale venture. Wholesalers must master relationship management, negotiate complex contracts, and think in terms of scalable operations.
What are the Types of Wholesale Businesses?

Wholesale businesses buy products in bulk from manufacturers and sell them to retailers, distributors, or other businesses at discounted prices. The 8 primary types differ by inventory handling, risk, and distribution approach, enabling various supply chain roles.
- Distributors: Manage full distribution networks, storing large inventories, handling logistics, marketing, and sales to retailers across regions. They often provide credit terms and after-sales support. Example: Sysco distributing food to restaurants nationwide.
- Manufacturers (Direct Wholesalers): Produce goods and sell directly in bulk to retailers or businesses, controlling pricing and branding while bypassing middlemen. Common for branded products. Example: Procter & Gamble wholesaling consumer goods to supermarkets.
- Merchant Wholesalers: Purchase goods outright from manufacturers, take ownership, store inventory in warehouses, and resell in smaller quantities to retailers. They bear all risks like spoilage or market shifts but offer competitive pricing. Example: Food distributors supplying supermarkets with bulk perishables.
- Cash-and-Carry Wholesalers: Operate warehouse-style stores where retailers visit, select bulk items, pay cash upfront, and transport goods themselves. No credit or delivery provided, minimizing wholesaler risk. Example: Costco or Restaurant Depot for restaurant owners buying ingredients.
- Drop Ship Wholesalers: Act as intermediaries without holding inventory; retailers list products, and the wholesaler forwards orders directly to manufacturers for shipment to end customers. Low overhead but reliant on supplier reliability. Example: Online electronics stores partnering with drop-ship suppliers.
- Brokers/Agents: Facilitate deals between manufacturers and buyers without taking title or inventory risk, earning commissions on transactions. They focus on negotiation and matchmaking. Example: Agricultural brokers connecting farmers to food processors.
- Direct-to-Retail Wholesalers: Manufacturers sell large volumes directly to major retailers, bypassing traditional middlemen for cost efficiency and control. Common for high-volume brands. Example: Apple supplying Walmart directly with electronics.
- Hybrid Wholesalers: Combine multiple models, such as traditional distribution for big retailers alongside drop-shipping for smaller ones or direct sales via owned ecommerce. Offers flexibility for scaling. Example: Brands using distributors for chains while drop-shipping to independents.
How to Start a Wholesale Business online
Choosing Your Wholesale Product Niche
Product Selection Criteria
Selecting the right product niche is critical to your wholesale success. Before sourcing inventory, evaluate these key factors:
Market Demand and Seasonality: Analyze whether your chosen product has consistent year-round demand or peaks seasonally. Research current market trends using tools like Google Trends, industry reports, and competitor analysis.
Profit Margins and Shipping Considerations: Calculate realistic profit margins by factoring in product cost, overhead, and shipping expenses. Products with higher value-to-weight ratios are typically more profitable for wholesale, as shipping costs significantly impact margins.
Purchase Frequency and Competition Analysis: Determine how often retailers would reorder your products. Consumables and trending items generate repeat orders, creating predictable revenue streams.
Leveraging Personal Expertise: Your existing knowledge, network, or passion becomes a competitive advantage. Choosing a niche where you have domain expertise reduces learning curves and builds credibility.

Trending Wholesale Business Ideas in 2026
Aligning with market trends increases your chances of success. These categories show strong wholesale potential:
- Health and Wellness: Supplements, fitness equipment, and organic personal care products
- Sustainable Fashion: Eco-friendly clothing and athleisure segments
- Home Décor: Eco-friendly home goods and personalized décor items
- Pet Supplies: Premium pet products and accessories
- Food and Beverage: Specialty foods, organic products, and beverages
- Educational Materials: Online learning resources and educational supplies
Setting Up Your Wholesale Business
Register Your Business and Legal Considerations
Before sourcing products, establish your business legally and compliantly.
Choosing a Business Entity:
- Sole Proprietorship: Simplest to start, but offers no liability protection
- LLC (Limited Liability Company): Provides personal liability protection and tax flexibility; recommended for most beginners
- S-Corporation: Best for scaling operations with higher anticipated revenues
Obtaining Necessary Licenses and Permits:
- Wholesale License or Resale Certificate: Required to purchase goods tax-free from manufacturers
- EIN (Employer Identification Number): Obtained from the IRS for tax purposes
- Sales Tax Permit: Necessary if you operate in states with sales tax obligations
- Business License: Local business permits from your city or county
Creating a Business Plan
Target Market Identification: Define your ideal retail customers. Are you targeting independent boutiques, online retailers, restaurants, or large chain stores?
Pricing Strategy: Factor in product cost from manufacturers, operational expenses, and desired profit margin (typically 50%+ for sustainable wholesale operations).
Operational Planning: Detail your warehousing and distribution approach, fulfillment timelines, and financial projections for the first three years.
Ready to start your wholesale journey? Sign up for Shopify’s free trial and explore their B2B wholesale features today. For advanced wholesale automation and inventory management solutions, consider platforms like B2Bridge that integrate seamlessly with Shopify to streamline your wholesale operations from day one.
Finding and Vetting Wholesale Suppliers
Types of Wholesale Suppliers
- Manufacturers: Produce goods directly and offer the lowest per-unit costs but require large minimum order quantities (MOQs).
- Distributors: Purchase from multiple manufacturers and offer smaller MOQs with greater product variety.
- Importers/Exporters: Specialize in sourcing products internationally, providing access to global markets.
- Dropshipping Suppliers: Hold inventory and ship directly to your customers, eliminating warehousing needs.

Supplier Vetting Best Practices
Verify Credentials: Check business licenses, certifications, and references. Request documentation and independently verify legitimacy.
Evaluate Product Quality: Order and test samples before committing to bulk purchases. Assess quality consistency and packaging.
Assess Delivery Reliability: Ask about lead times, shipping reliability, and rush order handling. Delayed shipments damage retailer relationships.
Where to Find Suppliers
- Trade Shows and Industry Conferences: Meet suppliers face-to-face and negotiate directly
- Online Supplier Databases: Platforms like Global Sources and TradeKey
- Wholesale Marketplaces: Faire, Alibaba, and industry-specific directories
- Direct Manufacturer Websites: Research companies directly
- Industry Associations: Many maintain supplier directories
Building Your Online Wholesale Store on Shopify
Shopify’s B2B Features for Wholesale
Shopify offers built-in B2B capabilities designed specifically for wholesale operations:
Company Profiles and Multi-Account Management: Manage multiple buyer accounts under one company umbrella with individual permission levels and custom pricing.
Customized Catalogs and Price Lists: Create customer-specific product catalogs visible only to designated wholesale buyers.
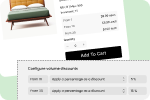
Volume and Tiered Pricing: Automatically adjust prices based on order quantity. For example:
- 1-50 units: $50/unit
- 51-200 units: $45/unit
- 200+ units: $40/unit
Protecting Your Pricing and Customer Segmentation
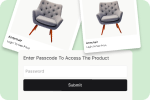
Hide Wholesale Prices from Retail Shoppers: Use Shopify’s customer segmentation to show wholesale pricing only to authenticated buyers.
Implement Minimum Advertised Price (MAP) Policies: Establish agreements that retailers won’t advertise below your suggested retail price.
Use Password Protection: Require login credentials for wholesale pricing access, signaling professionalism to business customers.
Set Your Wholesale Pricing and Payment Strategies
Wholesale Pricing Models
Profit Margin Targets: Most successful wholesalers target 50%+ margins (if a product costs you $10, sell it to retailers for $20). However, margins vary by industry.
Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price (MSRP): Know the MSRP for your products (typically 2-3x your wholesale cost) to guide pricing and help retailers understand margin potential.
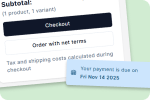
Setting Payment Terms
Net Payment Terms: Offering terms like Net 15, Net 30, or Net 60 is standard in wholesale and increases competitiveness.
Credit Policies: Establish formal credit policies. Check references and payment history before extending Net terms.
Payment Methods: Accept multiple payment methods (credit cards, bank transfers, ACH) to reduce friction.
Marketing and Selling Wholesale Products
Finding Wholesale Customers
Leverage Your Website: Add clear calls-to-action directing retailers to apply for wholesale accounts.
Join Wholesale Marketplaces: List products on platforms like Faire and ThomasNet with built-in buyer traffic.
Attend Trade Shows: Meet retailers face-to-face and secure orders directly.
Strategic Outreach: Directly contact boutiques and retailers that align with your products.
Using Incentives to Motivate Buyers
Volume Discounts: Offer special discounts for large commitments (“Order 500+ units and receive an additional 5% discount”).
Free Shipping Thresholds: Offer free shipping on orders over $1,000 to increase average order value.
First-Order Discounts: Offer new wholesale customers 10-15% off their first order.
Managing Wholesale Operations
Inventory and Warehouse Management
Demand Forecasting: Use historical sales data and market trends to forecast demand and plan inventory.
Inventory Management Software: Implement dedicated software like Cin7 or Shopify’s built-in tools for tracking and alerts.
Third-Party Logistics (3PL): As you scale, 3PL providers become cost-effective for storage and fulfillment.
Automating Operations with Technology
Order Processing: Automate order routing from Shopify to fulfillment systems.
Inventory Sync: Use APIs and automation tools to sync inventory across platforms.
Automated Invoicing: Generate invoices automatically and set up payment reminders.

Key Success Metrics to Track
Monitor these metrics to evaluate business health:
- Order Volume and Growth Rate: Track monthly trends
- Customer Retention Rate: High retention (60%+) indicates satisfaction
- Average Order Value: Monitor revenue per order
- Days Sales Outstanding (DSO): Measure payment speed
- Gross Margin Percentage: Track profitability
- Customer Acquisition Cost vs. Lifetime Value: Ensure LTV exceeds CAC by 3:1
Common Wholesale Myths Debunked
Myth 1: You Need Massive Upfront Capital
Reality: Many successful wholesalers started with $5,000-$25,000 using dropshipping or limited inventory strategies.
Myth 2: You Need an Extensive Network
Reality: Relationships can be built through trade shows, industry forums, and direct outreach.
Myth 3: Wholesale Requires Physical Warehousing
Reality: 3PL providers and dropshipping eliminate this requirement.
How to become a Wholesaler FAQ
Yes. Shopify supports wholesale through Shopify Plus B2B features or apps that offer custom pricing, minimum order quantities, company accounts, and bulk ordering. You can create restricted wholesale storefronts, price lists, and approval-based customer access to sell directly to business buyers.
You don’t legally need an LLC to start wholesaling, but forming one is recommended. An LLC provides liability protection, credibility with suppliers, and easier tax management. Some wholesalers may require a business license or resale certificate, which an LLC helps you obtain.
To qualify as a wholesaler, you typically need to register a legal business, obtain a resale certificate, and build relationships with suppliers or manufacturers. Wholesalers must also meet minimum purchase requirements, maintain inventory, and demonstrate the ability to sell in bulk to retailers or businesses.
Yes, reselling on Shopify is legal as long as you follow copyright, trademark, and brand distribution rules. You may need a resale certificate to buy from suppliers tax-free. Avoid selling counterfeit or restricted products, and ensure supplier agreements allow resale.
Conclusion
How to become a wholesaler on Shopify is an achievable goal for beginners with clear strategy and execution. The wholesale business model offers sustainable profits through volume sales and loyal customer relationships – fundamentally different from retail but equally rewarding.
Your action plan:
- This week: Validate your product niche and research suppliers
- Next 2-4 weeks: Register your business, set up Shopify, and prepare initial inventory
- Months 2-3: Launch your wholesale store and begin retailer outreach
- Months 4+: Refine operations and scale based on results
The wholesale landscape offers tremendous opportunities for entrepreneurs who combine market insight, operational discipline, and genuine customer focus. Shopify’s B2B tools make building a professional wholesale operation more accessible than ever.
Hi, I’m Ha My Phan – an ever-curious digital marketer crafting growth strategies for Shopify apps since 2018. I blend language, logic, and user insight to make things convert. Strategy is my second nature. Learning is my habit. And building things that actually work for people? That’s my favorite kind of win.