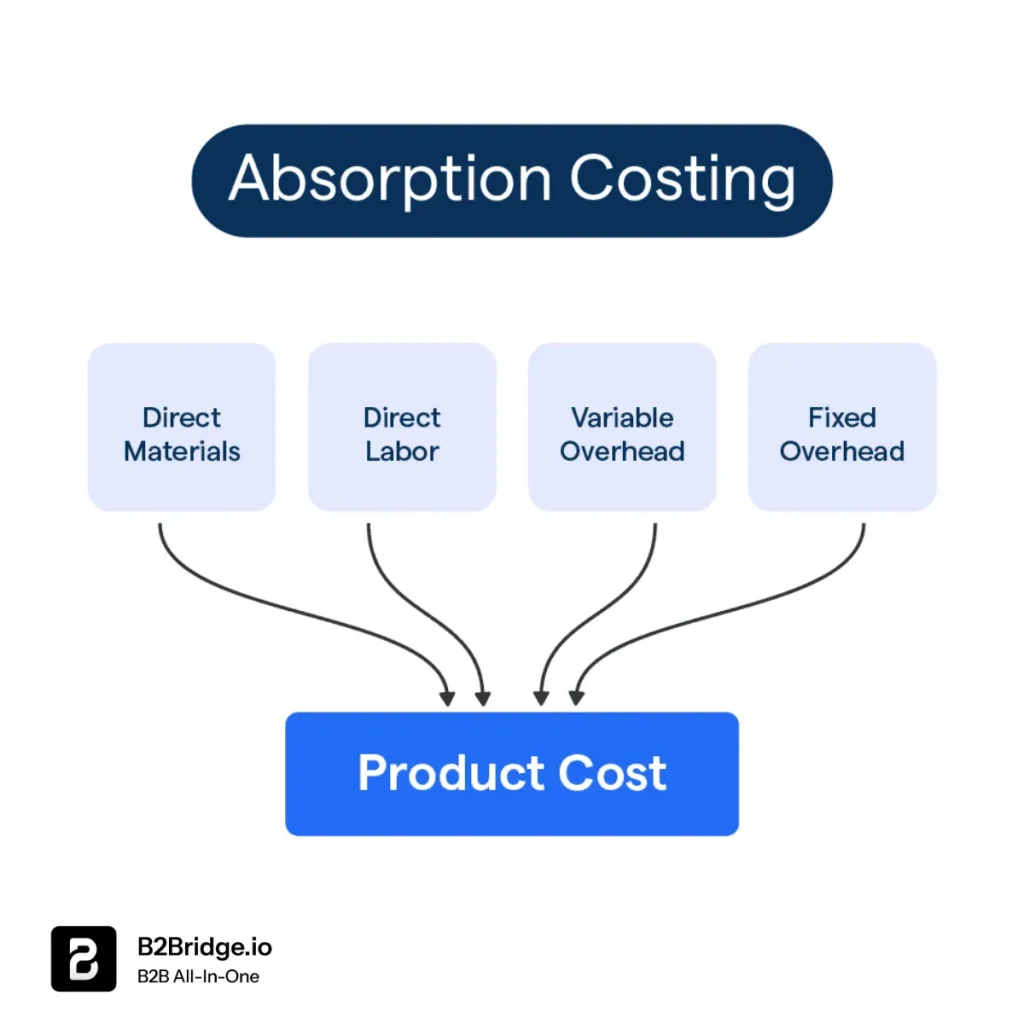
The absorption costing formula calculates a product’s total cost by adding direct materials, direct labor, and both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead, then dividing by the number of units produced, so all production costs are included in the product value.
Example: If a company incurs $200.000 in materials, $100.000 in labor, $60.000 in variable overhead, and $160.000 in fixed overhead, to produce 10.000 units, the calculation is:
($200.000 + $100.000 + $60.000 + $160.000) / 10.000 units = $52 per unit
This article will demystify the absorption costing formula through clear explanations, practical step-by-step calculations, proven tips, and real-world examples to provide the comprehensive insights you need.
What is Absorption Costing?
Absorption costing, also known as full costing or traditional costing, represents a costing method that assigns all manufacturing costs to products. Unlike variable costing, which only allocates variable manufacturing costs to products, absorption costing includes both variable and fixed manufacturing overhead costs in the product cost calculation.
This approach ensures that every unit produced carries its fair share of all manufacturing expenses, from raw materials and direct labor to factory rent, equipment depreciation, and supervisor salaries. The fundamental principle behind absorption costing is that all manufacturing costs – regardless of their behavior patterns – contribute to bringing a product to its finished state and should therefore be included in the product’s cost.

The key distinction between absorption costing and variable costing lies in the treatment of fixed manufacturing overhead. While variable costing treats fixed manufacturing overhead as a period expense (expensed in the period incurred), absorption costing spreads these fixed costs across all units produced during the period. This difference significantly impacts inventory valuation, cost of goods sold calculations, and reported profits, especially when production levels fluctuate.
For manufacturers, service providers, and businesses involved in production, understanding the absorption costing formula isn’t just an academic exercise – it’s a critical business skill that directly impacts profitability analysis, pricing strategies, and compliance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP). Whether you’re calculating the cost of a single product or managing complex multi-product manufacturing operations, mastering this formula ensures your business makes informed financial decisions.
>> Read more: 15 Best Wholesale Pricing Strategies to Boost Sales in 2026
Absorption Costing Formula Explained
The absorption costing formula serves as the mathematical foundation for calculating the complete cost of manufacturing each unit. The standard absorption costing formula is:
Absorption Cost per Unit = (Direct Materials + Direct Labor + Variable Manufacturing Overhead + Fixed Manufacturing Overhead) / Number of Units Produced
This straightforward formula encompasses all manufacturing costs and distributes them evenly across all units produced during a specific period. Let’s break down each component to understand its role in the calculation:
Direct Materials represent the most tangible cost element, typically the largest component of product costs. These costs are usually the easiest to calculate since they can be directly traced to products through material requisition forms, purchase orders, and inventory tracking systems.
Direct Labor includes wages, benefits, and payroll taxes for employees directly involved in production. Modern manufacturing often uses sophisticated time-tracking systems to accurately allocate labor costs to specific products or production runs.
Variable Manufacturing Overhead refers to indirect production costs that fluctuate with changes in production volume. These include expenses like indirect materials, factory supplies, utilities, and wages for additional labor required during increased output.
Manufacturing Overhead presents the most complex element of the formula, requiring careful calculation and allocation. This component includes all manufacturing costs that cannot be directly traced to specific products.
To calculate manufacturing overhead per unit, businesses typically use predetermined overhead rates based on allocation bases such as:
- Machine Hours: Appropriate when production is heavily automated
- Direct Labor Hours: Suitable when production is labor-intensive
- Direct Labor Dollars: Used when wage rates vary significantly among workers
- Units Produced: Simple method for homogeneous products
- Material Dollars: Effective when material costs correlate with overhead usage
The overhead allocation process involves two critical steps:
- Calculate the Predetermined Overhead Rate: Predetermined Overhead Rate = Estimated Total Manufacturing Overhead / Estimated Total Allocation Base
- Apply Overhead to Products: Applied Overhead = Predetermined Overhead Rate x Actual Allocation Base Used
Accuracy in overhead allocation is crucial because misstatements can significantly distort product costs, leading to poor pricing decisions and incorrect profitability analysis. Regular reviews of overhead rates ensure they reflect current cost structures and production patterns.
Comparison of Absorption Costing vs Variable Costing
Here is a comparison table of Absorption Costing vs. Variable Costing based on verified accounting principles:
| Aspect | Absorption Costing | Variable Costing |
| Cost Inclusion | Includes all manufacturing costs: direct materials, direct labor, variable and fixed overhead. | Includes only variable manufacturing costs: direct materials, direct labor, variable overhead. Fixed overhead is treated as a period cost. |
| Treatment of Fixed Manufacturing Overhead | Fixed overhead is assigned to product cost and inventoried. | Fixed overhead is expensed in the period incurred (period cost). |
| Cost per Unit | Higher, includes fixed overhead allocated per unit. | Lower, excludes fixed overhead from product cost. |
| Income Statement Format | Traditional format: Sales – Cost of Goods Sold (including fixed overhead) = Gross Profit. | Contribution margin format: separates variable and fixed costs. |
| Inventory Valuation | Inventories include fixed and variable manufacturing costs. | Inventories include only variable manufacturing costs. |
| Profit Impact | Profit can be influenced by production volume due to fixed overhead allocation to inventory. | Profit directly reflects sales volume since fixed overhead is expensed immediately. |
| GAAP Compliance | Required for external financial reporting (GAAP/IFRS). | Not allowed for external reporting; used for internal decision-making. |
| Usefulness | Better for pricing and external reporting. | Better for managerial decision-making and cost-volume-profit analysis. |
Step-by-Step Absorption Costing Calculation with Examples
Understanding the absorption costing formula becomes clearer through practical examples. Let’s walk through both simple and complex scenarios to demonstrate how these calculations work in real business situations.
Simple Example: Single Product Manufacturing
Scenario: ABC Manufacturing produces wooden chairs. During January, they produced 1,000 chairs with the following costs:
Step 1: Identify Direct Costs
- Direct Materials: $15,000 (wood, screws, glue)
- Direct Labor: $8,000 (carpenter wages and benefits)
Step 2: Calculate Manufacturing Overhead
- Variable Manufacturing Overhead: $3,000 (electricity, indirect materials)
- Fixed Manufacturing Overhead: $4,000 (factory rent, equipment depreciation)
- Total Manufacturing Overhead: $7,000
Step 3: Apply the Absorption Costing Formula Absorption Cost per Unit = ($15,000 + $8,000 + $7,000) / 1,000 = $30,000 / 1,000 = $30 per chair
Comparison with Variable Costing: Under variable costing, the cost per unit would be: Variable Cost per Unit = ($15,000 + $8,000 + $3,000) / 1,000 = $26 per chair
The $4 difference represents the fixed overhead allocation ($4,000 ÷ 1,000 units).
>> Try calculating your absorption costing with B2Bridge’s calculator:
Absorption Costing Calculator
Absorption Costing Calculator
Calculate Absorption Cost per Unit using the
formula:
(Direct Materials + Direct Labor + Variable Manufacturing Overhead +
Fixed Manufacturing Overhead) ÷ Number of Units Produced
Tip: Ensure the units produced is greater than 0. Fixed overhead is included in absorption costing and spreads across units produced.
Complex Example: Multiple Products with Different Overhead Drivers
Scenario: XYZ Electronics manufactures two products: smartphones and tablets. They use activity-based overhead allocation with multiple drivers.
Production Data for March:
- Smartphones: 2,000 units
- Tablets: 500 units
- Total Direct Materials: $200,000 (Smartphones: $160,000, Tablets: $40,000)
- Total Direct Labor: $75,000 (Smartphones: $50,000, Tablets: $25,000)
Manufacturing Overhead Allocation:
- Machine Setup Costs: $15,000 (allocated based on number of setups)
- Smartphones: 20 setups, Tablets: 10 setups
- Rate: $500 per setup ($15,000 ÷ 30 setups)
- Quality Inspection: $12,000 (allocated based on inspection hours)
- Smartphones: 200 hours, Tablets: 100 hours
- Rate: $40 per hour ($12,000 ÷ 300 hours)
- Facility Costs: $18,000 (allocated based on direct labor dollars)
- Rate: $0.24 per direct labor dollar ($18,000 ÷ $75,000)
Overhead Allocation:
Smartphones:
- Setup Costs: 20 × $500 = $10,000
- Quality Inspection: 200 × $40 = $8,000
- Facility Costs: $50,000 × $0.24 = $12,000
- Total Overhead: $30,000
Tablets:
- Setup Costs: 10 × $500 = $5,000
- Quality Inspection: 100 × $40 = $4,000
- Facility Costs: $25,000 × $0.24 = $6,000
- Total Overhead: $15,000
Final Absorption Cost Calculations:
Smartphones: Cost per Unit = ($160,000 + $50,000 + $30,000) / 2,000 = $240,000 / 2,000 = $120
Tablets: Cost per Unit = ($40,000 + $25,000 + $15,000) / 500 = $80,000 / 500 = $160
This complex example demonstrates how different overhead allocation methods can significantly impact product costs, emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate allocation bases that reflect actual resource consumption patterns.
Benefits and Limitations of Absorption Costing
Understanding both the advantages and drawbacks of absorption costing helps businesses make informed decisions about when and how to use this costing method effectively.
Key Benefits of Absorption Costing
GAAP and IFRS Compliance: Absorption costing is required for external financial reporting under both GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards. This compliance ensures that financial statements accurately reflect inventory values and cost of goods sold, providing stakeholders with reliable financial information.
Complete Product Cost Visibility: By including all manufacturing costs in product calculations, absorption costing provides managers with a comprehensive view of what it truly costs to produce each unit. This complete picture supports better pricing decisions and helps identify products that may not be covering their full manufacturing costs.
Proper Inventory Valuation: Absorption costing ensures that inventory on the balance sheet includes both variable and fixed manufacturing costs, providing a more accurate representation of the company’s investment in inventory. This is particularly important for companies with significant fixed manufacturing overhead or seasonal production patterns.
Long-term Decision Support: For strategic planning and long-term pricing decisions, absorption costing provides valuable insights by ensuring that all manufacturing costs are considered. This helps prevent the mistake of setting prices that cover variable costs but fail to contribute adequately to fixed cost recovery.
Performance Measurement: Absorption costing can help evaluate the performance of production managers by showing how well they control all manufacturing costs, not just variable costs. This comprehensive view supports more effective cost control initiatives.

Limitations and Potential Drawbacks
Fixed Overhead Allocation Distortions: The allocation of fixed manufacturing overhead can create artificial cost differences between products, especially when allocation bases don’t accurately reflect actual resource consumption. This can lead to misleading product profitability analysis and poor pricing decisions.
Production Volume Impact: Absorption costing can create incentives for managers to overproduce inventory to spread fixed costs over more units, temporarily improving reported profits while potentially creating inventory management problems and cash flow issues.
Limited Short-term Decision Value: For short-term decisions like special orders or make-or-buy analysis, absorption costing may not provide the most relevant information since it includes fixed costs that may not change with the decision.
Complexity in Multi-product Environments: As businesses produce more diverse product lines, the challenge of accurately allocating overhead becomes increasingly complex and potentially arbitrary, reducing the reliability of cost information.
Potential for Manipulation: Because absorption costing ties fixed cost absorption to production levels, it can be manipulated through production scheduling decisions, potentially distorting performance measurements and incentivizing suboptimal behavior.
Appropriate Use Cases
Absorption costing works best in environments with:
- Stable production levels and predictable overhead costs
- Products that consume overhead resources in proportion to the chosen allocation base
- Long-term pricing and strategic planning needs
- Requirements for GAAP-compliant external reporting
- Manufacturing operations where fixed costs represent a significant portion of total costs
Industries such as automotive manufacturing, furniture production, and traditional manufacturing operations often find absorption costing most suitable, while service industries or businesses with highly variable cost structures may benefit more from alternative costing methods.
Free Online Absorption Costing Calculators and Tools
To streamline absorption costing calculations and reduce the risk of errors, several free online calculators and tools are available. These resources can significantly speed up your costing processes while ensuring accuracy.
Recommended Free Calculators
Wall Street Mojo Costing Calculator: Features an intuitive interface with built-in formulas for various costing methods, including absorption costing. The tool allows for multiple product calculations simultaneously and generates downloadable reports. Particularly useful for educational purposes and small business applications.
Corporate Finance Institute (CFI) Templates: While not a calculator per se, CFI offers free Excel templates that include pre-built absorption costing formulas with professional formatting. These templates are particularly valuable for businesses that need to integrate costing calculations with their existing spreadsheet workflows.
Calculator.net Business Calculators: Provides a simple, straightforward absorption costing calculator with clear input fields and instant results. The tool includes basic overhead allocation features and is ideal for quick calculations and learning purposes.
>> Try calculating your absorption costing in seconds with our free calculator:
Absorption Costing Calculator
Absorption Costing Calculator
Calculate Absorption Cost per Unit using the
formula:
(Direct Materials + Direct Labor + Variable Manufacturing Overhead +
Fixed Manufacturing Overhead) ÷ Number of Units Produced
Tip: Ensure the units produced is greater than 0. Fixed overhead is included in absorption costing and spreads across units produced.
Integration Tips and Best Practices for Absorption Costing
When using online calculators, consider these recommendations:
Verify Calculations: Always double-check results using manual calculations or alternative tools, especially for significant business decisions. Online calculators should supplement, not replace, your understanding of the underlying formulas.
Maintain Documentation: Keep records of the inputs used in online calculators, including the specific tool version and date of calculation. This documentation supports audit trails and future reference.
Regular Updates: Ensure that the overhead rates and cost data you input into calculators reflect current business conditions. Outdated information can lead to inaccurate costing decisions.
Integration Considerations: For businesses using accounting software, explore how calculator outputs can be integrated with your existing systems. Many modern accounting platforms include built-in costing modules that can eliminate the need for separate calculator tools.
Case Study: Applying Absorption Costing in a Manufacturing Business
Background: Premier Furniture Manufacturing produces custom dining room sets in their 50,000 square foot facility. The company has struggled with accurate product costing and pricing, leading to concerns about profitability on different product lines.
Challenge: The company produces three main product lines – basic sets, premium sets, and luxury sets – but has been using a simple overhead allocation method based solely on direct labor hours, which doesn’t accurately reflect the different overhead requirements of each product line.
Solution Implementation: Premier Furniture decided to implement a more sophisticated absorption costing approach using multiple allocation bases:
Step 1: Cost Analysis During Q2, the company incurred the following costs:
- Direct Materials: $180,000 (Basic: $60,000, Premium: $70,000, Luxury: $50,000)
- Direct Labor: $120,000 (Basic: $40,000, Premium: $50,000, Luxury: $30,000)
- Manufacturing Overhead: $90,000
Step 2: Overhead Allocation Base Selection After analyzing their operations, they identified three primary overhead cost pools:
- Machine Operations: $40,000 (allocated by machine hours)
- Quality Control: $25,000 (allocated by inspection time)
- Facility Costs: $25,000 (allocated by floor space used)
Step 3: Data Collection
- Production: Basic (200 sets), Premium (150 sets), Luxury (100 sets)
- Machine Hours: Basic (800), Premium (900), Luxury (700)
- Inspection Hours: Basic (100), Premium (200), Luxury (300)
- Floor Space: Basic (40%), Premium (35%), Luxury (25%)
Step 4: Overhead Rate Calculations
- Machine Operations Rate: $40,000 ÷ 2,400 hours = $16.67 per machine hour
- Quality Control Rate: $25,000 ÷ 600 hours = $41.67 per inspection hour
- Facility Cost Rate: $25,000 ÷ 100% = $250 per percentage point
Step 5: Product Cost Calculations
Basic Sets:
- Direct Materials: $60,000
- Direct Labor: $40,000
- Machine Operations: 800 × $16.67 = $13,336
- Quality Control: 100 × $41.67 = $4,167
- Facility Costs: 40% × $250 = $10,000
- Total Cost: $127,503
- Cost per Set: $127,503 ÷ 200 = $637.52
Premium Sets:
- Direct Materials: $70,000
- Direct Labor: $50,000
- Machine Operations: 900 × $16.67 = $15,003
- Quality Control: 200 × $41.67 = $8,334
- Facility Costs: 35% × $250 = $8,750
- Total Cost: $152,087
- Cost per Set: $152,087 ÷ 150 = $1,013.91
Luxury Sets:
- Direct Materials: $50,000
- Direct Labor: $30,000
- Machine Operations: 700 × $16.67 = $11,669
- Quality Control: 300 × $41.67 = $12,501
- Facility Costs: 25% × $250 = $6,250
- Total Cost: $110,420
- Cost per Set: $110,420 ÷ 100 = $1,104.20
Results and Lessons Learned: The new absorption costing approach revealed that luxury sets, despite lower material and labor costs, actually had the highest cost per unit due to intensive quality control requirements. This insight led to:
- Revised pricing strategies that better reflected true product costs
- Process improvements in luxury set production to reduce inspection time
- Better understanding of resource consumption patterns across product lines
- Improved profitability analysis and strategic decision-making
The case demonstrates how proper absorption costing implementation can provide crucial insights for business strategy and operational efficiency.
Tips for Accurate Absorption Costing Calculations
Achieving accuracy in absorption costing requires attention to detail and systematic approaches to cost tracking and allocation. Here are proven strategies for improving your costing accuracy:
Regularly Review and Update Overhead Rates: Manufacturing environments change continuously, with new equipment, process improvements, and cost structure modifications. Schedule quarterly reviews of your predetermined overhead rates to ensure they reflect current conditions. Compare actual overhead costs to applied overhead regularly to identify significant variances that might indicate the need for rate adjustments.
Choose Appropriate Allocation Bases: The selection of allocation bases significantly impacts cost accuracy. Analyze your production processes to identify the cost drivers that best correlate with overhead consumption. For example, if your production is highly automated, machine hours might provide better allocation accuracy than direct labor hours. Consider using multiple allocation bases for different overhead cost pools to improve precision.
Implement Robust Cost Tracking Systems: Invest in systems that can accurately capture and categorize costs as they occur. Modern manufacturing execution systems (MES) can provide real-time cost data and automatic allocation of overhead based on actual production activities. This real-time approach reduces the reliance on estimates and improves cost accuracy.
Monitor Inventory Levels Carefully: Under absorption costing, inventory levels directly affect profit reporting because fixed overhead costs are deferred in inventory. Establish inventory management procedures that ensure accurate quantity tracking and proper cost flow assumptions (FIFO, LIFO, or weighted average). Regular physical inventory counts help validate system accuracy.
Use Absorption Costing with Complementary Methods: While absorption costing is required for external reporting, consider using it alongside variable costing and activity-based costing for internal decision-making. This multi-faceted approach provides different perspectives on cost behavior and can lead to better business decisions.
Document Allocation Methods and Assumptions: Maintain clear documentation of your overhead allocation methods, including the rationale for allocation base selection and the calculation of predetermined rates. This documentation supports audit requirements, ensures consistency over time, and facilitates training of new personnel.
Perform Sensitivity Analysis: Test how changes in key assumptions (overhead rates, allocation bases, production volumes) affect your product costs. This analysis helps identify which cost elements have the greatest impact on your costing accuracy and where additional precision might provide the most value.
How B2Bridge Simplifies Wholesale Costing and Pricing on Shopify
For businesses selling through wholesale channels, accurate product costing becomes even more critical as pricing strategies must account for different customer segments and volume requirements. B2Bridge transforms how Shopify merchants manage their wholesale operations by providing sophisticated tools that complement absorption costing methodologies.
Simplify wholesale management: Run B2B as easily as B2C with B2Bridge’s all-in-one wholesale tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing cost accounting processes. The platform automatically applies your calculated absorption costs to different customer tiers, ensuring consistent pricing across all channels.
Protect your pricing: Hide wholesale prices from retail shoppers and show the right price to the right customer based on your absorption costing calculations. B2Bridge’s tiered pricing system allows you to implement cost-plus pricing strategies that reflect your true manufacturing costs while maintaining appropriate margins for different customer segments.

Offer a seamless buyer experience: Give your B2B buyers a smooth, self-serve shopping journey with prices that reflect accurate absorption costing. Professional buyers appreciate transparent pricing that they can rely on for their own planning and budgeting processes.
Close more wholesale deals: Turn requests for quotes into orders with built-in negotiation tools that respect your cost structure. B2Bridge allows you to set minimum acceptable margins based on your absorption costs, ensuring that negotiations don’t compromise profitability.
FAQs About Absorption Costing Formula
Activity-based costing (ABC) allocates overhead by tracking the specific activities that drive costs. It assigns each activity’s expenses to products or services based on how much they actually consume, giving a more accurate picture of indirect costs than traditional costing.
The absorption coefficient measures how much light a material absorbs relative to its thickness.
Formula: α = –ln(1 – percentage absorbed) ÷ material thickness
Use this formula:
Absorption Cost = (Direct_Labor + Direct_Materials + Variable_Manufacturing_Overhead + Fixed_Manufacturing_Overhead) / Number_of_Units_Produced
The primary difference lies in the treatment of fixed manufacturing overhead. Absorption costing includes fixed manufacturing overhead in product costs and inventory valuations, while variable costing treats fixed manufacturing overhead as a period expense. This difference affects inventory values, cost of goods sold, and reported profits, particularly when production levels vary from sales levels.
Manufacturing overhead allocation involves selecting an appropriate allocation base (such as machine hours, direct labor hours, or direct labor dollars), calculating a predetermined overhead rate by dividing estimated overhead by estimated allocation base activity, and then applying overhead to products by multiplying the rate by actual allocation base usage for each product.
Absorption costing provides valuable information for long-term pricing decisions by ensuring that all manufacturing costs are considered. However, for short-term pricing decisions (such as special orders), variable costing may provide more relevant information since it focuses on costs that actually change with the decision.
Absorption costing affects both the balance sheet and income statement. On the balance sheet, inventory values include both variable and fixed manufacturing costs. On the income statement, cost of goods sold reflects the full absorption cost of units sold, potentially creating differences in reported profits compared to variable costing, especially when production and sales volumes differ.
Absorption costing is typically preferred in traditional manufacturing industries with significant fixed overhead costs, such as automotive, furniture, and heavy equipment manufacturing. Service industries or businesses with minimal fixed manufacturing costs may find variable costing more useful for internal decision-making, though they still must use absorption costing for external reporting.
Conclusion
The key to successful absorption costing implementation lies in understanding that accuracy depends not just on mathematical precision, but on thoughtful selection of allocation bases, regular review of overhead rates, and integration with comprehensive cost management systems. Whether you’re calculating costs for a single product or managing complex multi-product operations, the principles and practices outlined in this article provide the framework for reliable cost information.
For businesses looking to leverage absorption costing in their wholesale operations, modern tools like B2Bridge offer sophisticated solutions that complement traditional costing methods with automated pricing management and customer segmentation capabilities.
Master absorption costing with our clear formula, practical examples, and free online calculators. Use B2Bridge to simplify your costing process and improve accuracy. Explore our pricing plans designed to fit your business needs. Contact us for expert support and personalized advice.
See how other businesses have succeeded with B2Bridge through our customer stories.
Hi, I’m Ha My Phan – an ever-curious digital marketer crafting growth strategies for Shopify apps since 2018. I blend language, logic, and user insight to make things convert. Strategy is my second nature. Learning is my habit. And building things that actually work for people? That’s my favorite kind of win.